- On the server’s side, there is a component called an SSH daemon that is constantly listening to a specific TCP/IP port for possible client connection requests. Once a client initiates a connection, the SSH daemon will respond with the software and the protocol versions it supports and the two will exchange their identification data.
- SSH is by default configured to listen to port 22, and only on port 22. You can configure your SSH server to run on other ports, and extending the same method, you can configure your SSH server to run on more than one ports.
Ssh Server Port Number
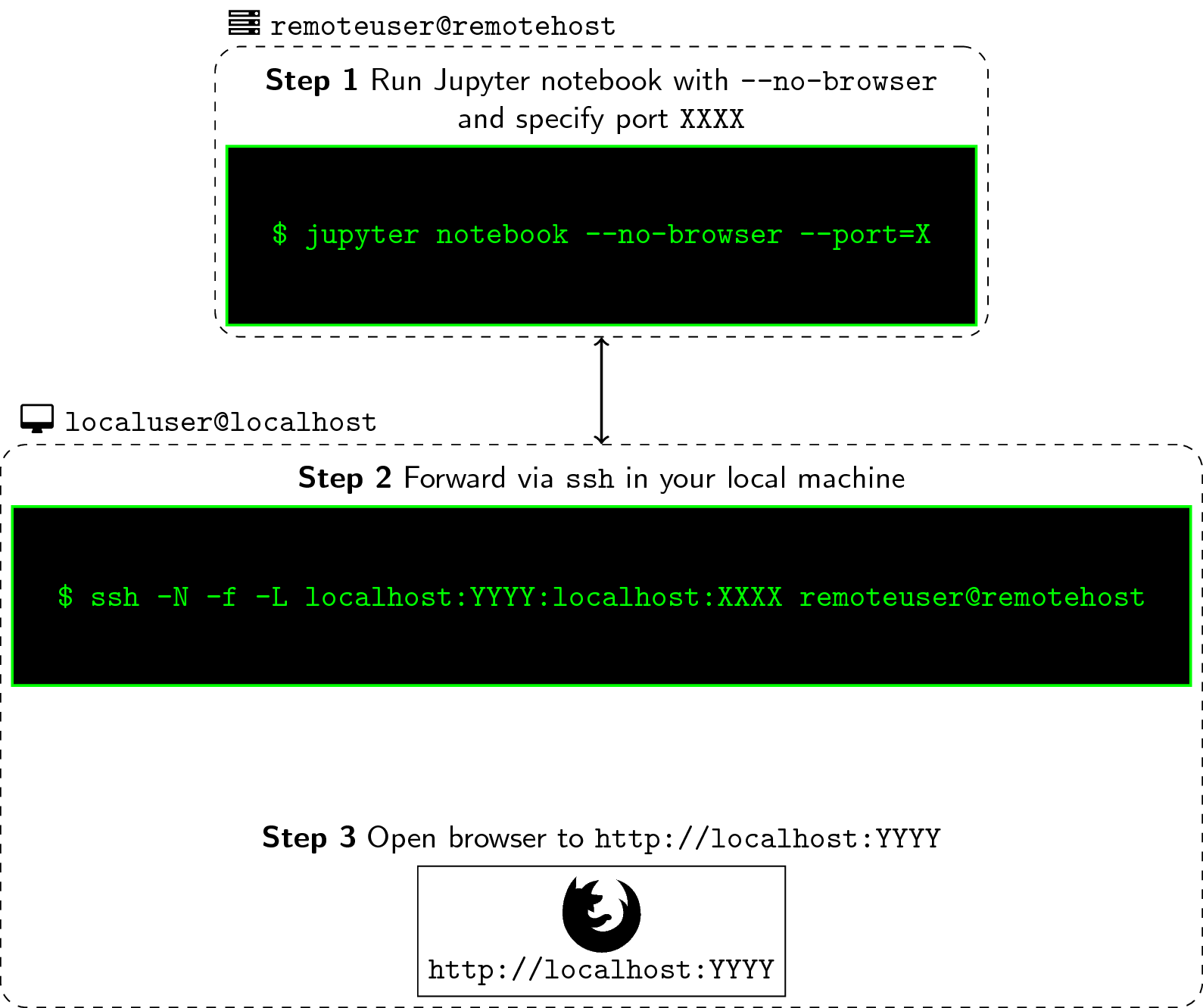
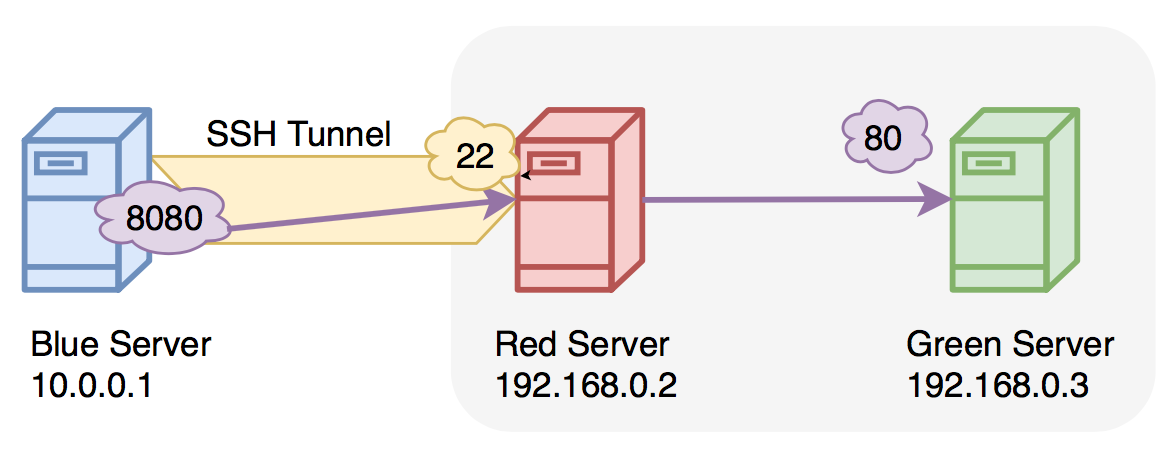
Nov 05, 2020 If you have access to a remote SSH server, you can set up a remote port forwarding as follows: ssh -R 8080:127.0.0.1:3000 -N -f user@remote.host. The command above will make the ssh server listen on port 8080, and tunnel all traffic from this port to your local machine on port 3000. Either edit /etc/ssh/sshdconfig & don't forget to restart SSH (service sshd restart) or leave it on 22, but forward port 26 on the router to port 22 on the second machine. Also, don't forget to change any firewall settings on the second machine to allow the connections through. When you connect to a server via SSH, most of the time you don't provide any port information. And in such cases, your connection goes to the port 22 of the SSH server. You can change the default port from 22 a port number of your choice using the following steps: Open the /etc/ssh/sshdconfig file for editing.
If you are aware of the SSH basics, you already know that SSH uses port 22 by default.
When you connect to a server via SSH, most of the time you don't provide any port information. And in such cases, your connection goes to the port 22 of the SSH server.
You can change the default port from 22 a port number of your choice using the following steps:
- Open the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile for editing. - Locate the line that has
Port 22(if it is commented out with #, remove the # as well). - Change the line to Port 2522 (or any number of your choice between 1024 and 65535).
- Make sure that the new port is allowed by the firewalls (if you have any).
- Restart ssh daemon with
sudo systemctl restart sshd. - From now onwards, you'll have to specify the port to make the ssh connection
ssh user@ip_address_of_server -p 2522.
Let me show you the steps in details and also tell you why you may consider changing the
Why change the default SSH port?
One of the most elementary tricks for securing SSH server is to change the default SSH port number 22.
Why? Because a number of bot scripts try the brute force attacks on the default port 22. Most of these scripts don't always scan for open ports, and they target the default ports for various known services like SSH.
Changing the default SSH port reduces number of such attacks. There are other ways to improve the security of your SSH server. If interested, please follow these actionable tips for improving SSH server security.
Now that you know why you would change the default SSH port, let's see how to do it.

Allow traffic on the new port by changing the firewall settings
If you have a firewall set or custom ipconfig or ifconfig or if you are using selinux, you must allow the new ssh port before making the changes. Otherwise you may lock yourself out without an SSH access.
Now this part depends upon what kind of firewall or routing you are using.

If you are using UFW, you can use the following command to allow port 2522:
If you are using iptables, you should use this command:
Ssh Server Port
On Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat, the firewall is managed by firewalld and you can use this command:
On CentOS and Red Hat, you may also have to change the SELinux rules:
Now that you have put the correct firewall settings, let's move on to changing the SSH port.
Changing the default SSH port
Usually, the ssh configuration file is located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config. You'll have to use a terminal-based editor like Vim or Nano or Emacs to edit the file.
Distributions like Ubuntu have Nano installed by default so you can use it for opening the file in edit mode like this:
As you can see, you'll have to be a sudo user or root to edit the ssh configuration.
Scroll down a bit and you'll see a line with Port 22. If it starts with #, it means the line is commented out. The commented out lines gives you the default settings.
So if you see # Port 22, it means that default port is 22.
Change this line with a port number of your choice. In Linux, port number 0-1023 are usually reserved for various services. It will be good to avoid using anything between 0 and 1023 to avoid conflicts.
You can use any other port number between 1024 and 65535. I am using 2522 in the example. Make sure to remove the # before the Port line.
Save your changes and exit the editor. If you are using Nano, use Ctrl+X to save and exit.
The next step is to restart the ssh service. Most modern system use systemd services so you can use the following command:
Now if you want to access the SSH server, you'll have to specify the port number:
Was it helpful?
I hope you find this tutorial helpful in changing the SSH port. Now that you have changed the port, you'll have to use it all the time you want to connect to the server via SSH and that could be annoying.
This is why I recommend using SSH config file to save the settings for easy and quick access.
Become a Member for FREE

Ssrs 2014 New Features
Join the conversation.
